The Seventh Annual AI Startup Landscape (2024)
In order to highlight the AI startup landscape in Germany, drive AI adoption and create more partnership opportunities between startups and corporations to enhance the overall knowledge on applied AI, every year the appliedAI Institute for Europe publishes the German AI Startup Landscape - Germany’s most important and detailed analysis of the AI Startup scene.
Together with the help of our partners from academia, government and industry, we have set out to create an ecosystem in which AI startups can flourish to help shape the future of AI for the benefit of society. By creating a centralised database of high-quality and externally validated AI startups, we provide easy access to enable connections between corporations and SMEs as well as governmental institutions to AI partners they can trust. For the second time, we are also happy to announce the most promising AI Startups in Germany, based on a voting among our highly renowned contributors.
Together with Deutsche Telekom, NVIDIA, Intel, UnternehmerTUM and eleven renowned venture capital firms (Cherry Ventures, Earlybird Capital, UVC Partners, Yttrium, High-Tech Founder Funds (HTGF), eCAPITAL, Burda Principal Investments, HV Capital, D11Z.Ventures, MIG Capital and AI.FUND), over 1000 startups were examined. All startups were founded in or after 2014 with a primary business model based on AI (cf. details on methodology below). All AI startups featured are headquartered in Germany.
By the way: We are now taking applications for the AI Startup Landscape 2025 - so if you’re a top-notch AI Startup and want to be featured on next year’s landscape, apply now!
How to use the Landscape
Below you can view all 687 startups sorted via their primary category within the clusters of Industry, Technology Type, Enterprise Intelligence or Enterprise Function.
You can also search for startups via their name or keywords found in their description. Hover over the logo and click the magnifying glass to read the full company description, or click the logo directly to head to the startups website and learn even more.
Below the map you can find a table with all startups listed with even more details including secondary categories. Head to the bottom of the page to see insights into the data and key learnings from the German AI startup ecosystem.
Methodology
Following academic standards, we developed a robust, strict and objective methodology for screening, analysing and evaluating all AI Startups in Germany. Overall, the process can be summarised as follows:
During the year, startups apply to be featured on the Landscape via our online survey. Moreover, we screened the entire German Startup Landscape and accepted nominations from our contributors (Deutsche Telekom, NVIDIA, Intel, UnternehmerTUM, Cherry Ventures, Earlybird Capital, UVC Partners, Yttrium, HTGF, eCAPITAL, Burda Principal Investments, HV Capital, D11Z.Ventures, MIG Capital and AI.FUND).
Startups are then evaluated based on data, talent, AI methods, scalability, overall quality and subsequently clustered (see “clustering logic” below). The startups are initially rated (‘shortlisted’ or ‘discarded’) by our AI Expert Team to create a shortlist. To enhance the validity of our results, all startups are evaluated by several experts. Unclear cases - i.e. startups evaluations where the experts disagreed - were then individually evaluated in a larger expert group, resulting in a final “shortlist” or “discard” decision.
Startups from the AI Startup Landscape of the previous year are automatically transferred to the new year iteration unless they have closed their business, were acquired, pivoted their business model away from AI or moved to a different geographical location outside of Germany. If a startup was on the previous year iteration but is now older than 10 years, it was also deleted.
In order for a startup to be approved for the AI Startup Landscape, they must meet the following requirements:
- Be a registered company.
- Have been founded less than 10 years ago or pivoted their core business model to AI less than 10 years ago (including 2014).
- The startup’s headquarter must be situated in Germany.
- They should have a minimum of two Full Time Equivalents (FTEs)
- They should have a minimum of one FTE with AI competence
- They should have AI at their core or exhibit a significant usage of AI.
- The start-up respectively its business model has a high face validity (e.g., professional website, convincing business model, etc.).
The shortlist is independently evaluated and rated by our jury (Deutsche Telekom, NVIDIA, Intel, UnternehmerTUM, Cherry Ventures, Earlybird Capital, UVC Partners, Yttrium, HTGF, eCAPITAL, Burda Principal Investments, HV Capital, D11Z.Ventures, MIG Capital and AI.FUND).
In a final step, all feedback received is then synthesised and analysed by the experts of the appliedAI Institute for Europe.
Clustering logic
The clustering logic is based on Shivon Zilis’ landscape of machine intelligence. It is developed from the point-of-view of companies that want to use AI in their businesses:
Enterprise Functions: Increasing productivity of existing tasks. Support your employees with ready-to-use, AI-enabled tools supporting their day-to-day work to increase productivity.
AI Capabilities: Exploiting new data sources. Tap into new insights that were previously too difficult or expensive to be gained through conventional methods.
Technology Type: Building products with ML. Give developers the tools that they need to build and leverage machine learning software to gain a competitive advantage.
Industries: Leveraging AI-first products: Use and cooperate with startups using machine learning to offer industry-related products and services.
Deeper Insights about the German AI Startups
Landscape Growth:
Following last year’s trend, we again see a massive surge in the number of AI Startups in Germany. There are 687 startups on the German AI Startup Landscape 2024 representing a 35% growth compared to the previous year. While this overall growth rate is impressive, it is significantly below last year’s growth rate of 67%. From 508 AI startups in the 2023 AI Startup Landscape, 467 remain on the list and 220 new AI startups were added to the list. Thus, the survival rate of AI Startups is extremely high compared to the survival rate of non-AI Startups. Out of 41 AI startups that are not represented on the German AI Startup Landscape 2024 anymore, 49% moved their headquarter outside of Germany, 17% were acquired, 10% are in liquidation, and 24% had to be removed as they were now older than 10 years. Noteworthy, almost all AI Startups that moved their headquarter outside of Germany established their new headquarter in the USA.

Overall, two things are worth mentioning regarding the AI Startup growth rate from our perspective: First, it needs to be noted that there is a discrepancy between the actual founding of an AI Startup and being featured on the AI Startup Landscape. The reason herefore is that only AI Startups are listed that display a strong business model with a certain number of FTE and internal AI competence (cf. sub-section “Methodology” for further information). As such, there is a time lag between the initial founding of an AI Startup and being featured in our list, as only high-quality AI startups are listed (and, in turn, AI startups with limited resources and unspecified value propositions are not yet listed as they are still in the progress of further development). Given the fact that more and more startups try to position themselves as “AI companies'' despite not actually having any internal AI competence, following our rigorous procedure seems more important than ever.
Secondly, the decelerating growth rate - although still on a very high overall level - may indicate a progression towards a more stable and sustainable growth pattern as the AI startup ecosystem matures and consolidates. The slower growth rate could also reflect a more cautious approach from investors (cf. sub-section “Funding” for further information). Moreover, while the EU AI Act might affect the decision of founders to establish their headquarters in Germany, it needs to be highlighted that no empirical conclusions can be made based on the existing data (neither regarding potential positive nor potential negative nor no effects of the EU AI Act on AI Startup founding activities). Establishing potential causality would require a longitudinal study.

Location:
As in the last editions, the cities of Berlin and Munich continue their domination in the AI Startup Landscape. The share of two cities amounts up to approximately 50% of German AI startups. This year, Berlin again clearly dominates as the German city with the largest number of AI startups (209), while Munich ranks in second place (136 including the suburbs of Munich). However, other cities are catching up with sometimes considerable growth numbers. Specifically, the following cities have a two-digit number of AI Startups: Hamburg (65), Karlsruhe (17), Stuttgart (16), Cologne (16), Darmstadt (16), Aachen (11), Düsseldorf (11), and Frankfurt (10).

On a federal state level, Berlin (30,4%) again clearly dominates the AI Landscape in Germany, followed by Bavaria (23,3%), Baden-Württemberg (11,5%), North Rhine-Westphalia (10,2%), and Hamburg (9,6%). Put differently, five federal states account for astonishing approximately 85% of the German AI Startups.

To establish a more meaningful interpretation of the results, the AI Startups per capita of a federal state should be considered. This leads to an interesting shift in the ranking. Specifically, while Berlin as a city state ranks first place again, it is followed by Hamburg, Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg, Saarland, and Hesse. The numbers highlight that there is a significant disparity between the federal states in Germany, with Berlin having approximately 100x more AI Startups than Saxony-Anhalt on a per capita basis. This highlights the very high geographical disparity of AI founding activities within Germany.
Funding:
Approximately 38% of the AI Startups listed in the AI Startup Landscape 2024 received a significant amount (> 1 million USD) of funding (subject to publicly available information). For the AI Startups with a funding larger than 1 million USD, the average amount of funding received is 17,1 million USD, whereas the median is 5,5 million USD. Notably, 80 AI startups received funding larger than 10 million USD. Moreover, 184 AI startups received funding between 1 and 10 million USD.
Taking a closer look only at the last funding round, 2023 was the record year with approximately 1.2 billion USD overall funding (including two major outliers), followed by 2022 (approx. 771 million USD).
It is noteworthy that investment activities into newly founded AI Startups continued to decline after 2021: While AI Startups founded in 2021 have received a total of approximately 535 million USD so far, the AI Startups founded in 2022 and 2023 combined received a cumulative funding amount of only approximately 93 million. While more mature AI Startups generally naturally are able to attract higher funding rounds, gathering capital seems challenging for recent founders (i.e. for AI Startups founded in 2022 or later).
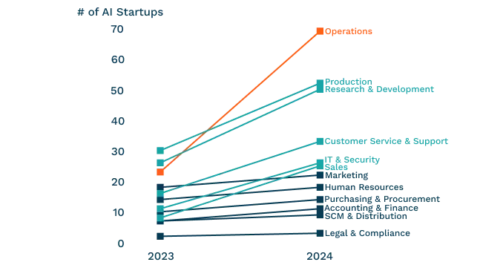
Industry sector and enterprise functions:
For the AI Startups with a clear industrial focus, this year we observe the most activities in the following German key industrial sectors: (1) Cross-Industry, (2) Human Health and Social Work Activities, (3) Manufacturing, and (4) Transportation, Mobility, & Storage. Compared to last year, it is noteworthy mentioning that there has been a surge in AI Startups focussing on cross-industry as well as manufacturing. This shift towards broader applications of AI technology indicates a maturing state of AI solutions, showing that they are increasingly capable of addressing complex, real-world problems across diverse industries.

The following figure shows the distribution of AI Startups among industries: On the Enterprise Function front, German AI startups are very active in the areas of Operations (70), Production (53), Research & Development (51), Customer Service & Support (34), IT & Security (27), and Sales (26). Compared to last year, the amount of AI Startups active in each Enterprise Function increased, often significantly. For example, the number of AI Startups active in operations and production combined more than doubled, which again underlines the growing potential to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve quality control in manufacturing and operational settings. The trend also indicates a shift towards more practical, industry-specific AI applications that can deliver tangible benefits to businesses across various sectors of the German economy.
Moreover, it is notable that almost all AI Startups analysed are B2B-Startups. Indeed, the trend seems to continue that only approximately 5% of the AI Startups are exclusively active in the fields of B2C or B2G.

Technology Type and Enterprise Intelligence:
Regarding the technology type, German AI Startups are predominantly active in developing Applications (173), followed by Platforms (136), Infrastructure (26), and Frameworks (20).
When it comes to the underlying AI Capabilities, German AI Startups are very strong especially in the fields of computer vision (22,1%) and natural language processing (19,7%). Moreover, AI Startups are active in planning (13,3%), creation (13%), discovery (12,5%), and forecasting (11,3%). 4,2% of the AI Startups analysed are predominantly active in the field of computer audition and 3,9% in the field of robotics.
Generative AI:
Generative AI is capable of generating new and unique content for various applications. These models are created by training a foundation model on large amounts of data and then fine-tuning it to improve its content generation capabilities. As such, a generative AI Startup focuses on leveraging generative AI technologies to develop innovative products, services, or solutions. These startups typically specialise in creating and deploying AI models, particularly those built upon foundation models, with the aim of generating unique and valuable content across various domains.
As part of this study and in order to enable an objective and data-driven classification of each AI Startup, we developed an AI-based generative AI classification system. This classification system evaluated which of the 687 AI Startups of this year’s landscape can be classified as working specifically on generative AI solutions. The results show that every fifth AI Startup is active in the field of generative AI. This significant proportion underscores the rapid proliferation of generative AI technologies within the startup ecosystem. However, German generative AI Startups are only able to get very limited funding: When excluding outliers (specifically, the top ten percent of the funded generative AI Startups), the remaining generative AI Startups attract approximately only 750.000 USD.
Highlighted AI Startups in Germany
The AI Startup scene in Germany is continuing to grow and new AI Startups are founded on an almost daily basis. Thus, to gain deeper insights into the race at the top, we are happy to announce the most promising AI Startups in Germany 2024. This list was compiled based on a voting of the jury (i.e. Deutsche Telekom, NVIDIA, Intel, UnternehmerTUM, Cherry Ventures, Earlybird Capital, UVC Partners, Yttrium, HTGF, eCAPITAL, Burda Principal Investments, HV Capital, D11Z.Ventures, MIG Capital and AI.FUND), where each contributor was allowed to nominate their picks. The final list was subsequently consolidated and ranked by the AI experts of the appliedAI Institute for Europe. The appliedAI Institute for Europe did not participate in the voting itself.
Based on the jury voting, the following startups were selected as being the most promising AI Startups in Germany for 2024 (please note that the order presented is alphabetically and non-hierarchical - AI Startups that were already in the list of the most promising AI Startups in Germany 2023 are highlighted):
Akirolabs GmbH
Aleph Alpha
Celus
Certivity
Cognigy
Constellr
dstack
FERNRIDE
Floy
FluIDect
Graswald.ai
Helsing
Kopernikus Automotive
Langdock
Langfuse
LiveEO
Orbem
OroraTech GmbH
paretos
Parloa
remberg GmbH
SPREAD
Synera
Tacto
Trail ML
Ultimate.ai
Wingcopter GmbH
Contributors














How you can use the AI Startup Landscape 2024
As a non-profit organisation, we believe that sharing high-quality knowledge is our obligation. Using this landscape as part of a presentation, talk, or project is allowed and encouraged as long as you always use the visual representation and reference us appropriately. Changes to the AI Startup Landscape 2024 have to be marked explicitly as your own changes. The content of this insight is published under CC-BY 4.0.
Contact us
We will be more than happy to discuss the insights of the AI Startup Landscape with you. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to contact us:

Contact us
Disclaimer
The data used in the AI Startup Landscape 2024 was collected and analysed to the best of our knowledge and understanding at the time of writing. While we strive to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented, it is possible that errors, omissions, or inaccuracies may exist. Therefore, we cannot guarantee the completeness, correctness, or timeliness of the information provided.
The content provided is intended for general informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional or legal advice. Any reliance you place on the information is strictly at your own risk. We recommend verifying any critical information through additional sources or consulting with appropriate experts before making decisions or taking actions based on the provided information.